The purpose of Variant management is the ability to define different process variants. Tasks can be filtered or turned on or off to process exactly one variant. Those variants can be defined and named via the dialog window Edit / Manage task filters ... (see chapter User Interface / Menu bar / Processing). Subsequent to this, those variants can be assigned to individual tasks or task groups. Before the simulation the user can decide, which of the defined variants he want to simulate and run.
1 |
Definition of the variants / task filters |
2 |
Selection of variants / task filters within the tasks |
3 |
Selection of the variant / task filter to be simulated |
4 |
Control field of the active variant / task filter assigned to the relevant task |
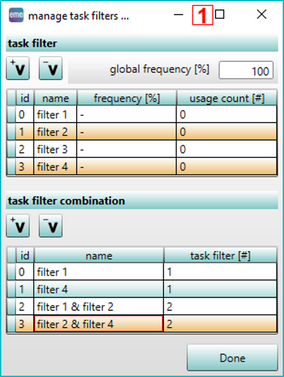
Figure 69: Definition of variants / task filters
In the first step task filters have to be defined on the dialog box Manage task filters ... The dialog is divided into two levels Task filter and Task filter combination, each consisting of 2 buttons and a table. In the upper level Task filters basic filters can be generated and removed using the corresponding buttons ![]() Add task filter and
Add task filter and ![]() Remove task filter. Multiple filters can be selected and deselected by pressing and holding down the Ctrl key and then clicking each filters that need to be selected or deselected. In the lower level Task filter combination a mix of of filters from the upper level can be added by clicking the lower button
Remove task filter. Multiple filters can be selected and deselected by pressing and holding down the Ctrl key and then clicking each filters that need to be selected or deselected. In the lower level Task filter combination a mix of of filters from the upper level can be added by clicking the lower button ![]() Add task filter combination. Filters can be removed by clicking
Add task filter combination. Filters can be removed by clicking ![]() Remove task filter combination. Selection changes in one level is reflected in the other level according to their filter names. By clicking on the respective fields in the column Name filter or filter combinations can be renamed. By clicking on the column headers, the rows are sorted according to their entries.
Remove task filter combination. Selection changes in one level is reflected in the other level according to their filter names. By clicking on the respective fields in the column Name filter or filter combinations can be renamed. By clicking on the column headers, the rows are sorted according to their entries.
The documentation and evaluation of the Proportional tasks (tasks executed irregularly) are possible by specifying frequencies (column Frequency [%]) for task filter (variants), Global frequency (%] and intervals for tasks (see chapter Parameter types / User defined parameters / User defined task parameters -> Table parameter Interval). The frequencies/intervals defined per tasks are combined and converted into a Proportional factor. It is in the section User interface / Tabs "Tasks" / Proportional tasks description.
The value Global frequency [%] can be used to define the actual frequency of the processes represented in the simulation, in order to derive the corresponding results in the evaluations. (For example, to simulate proportional tasks or program adjustments).
The Done button closes the dialog box.
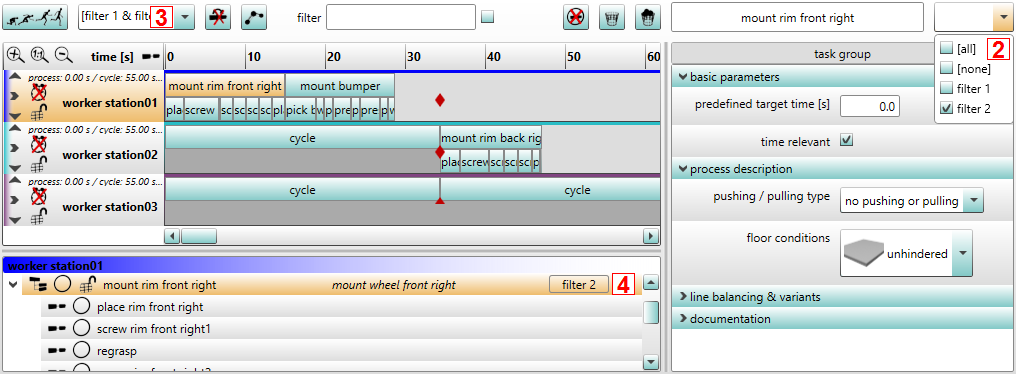
Figure 70: Usage of variants
In the second step the desired task filter can be assigned to the corresponding task via the drop-down box above the task parameters. For that purpose the basic filters Task filter from the top of the dialog described in step 1 are provided.
In the third step a combination of task filters can be chosen right next to the Simulate button. One of the Task filter combination entries defined on the bottom of the dialog described in step 1 can be chosen to activate the desired task filters.
In the fourth step, the corresponding Task filter name is displayed to the right side of the tasks within the task list for monitoring purposes. After selecting the Task filter combination (Step 3) inactive tasks are greyed out in the task list and are hidden in the time line. Active tasks are displayed in black text color as usual. In the simulation only active tasks will be executed.