Coordinate parameters / markers define points along with orientation in 3D space. They are used to define geometrical targets for the human model. Also, this can be used to define the target points for grasping, walking, tool center points, to position the camera, focal or starting points etc.
By means of a left click on the button ![]() Add marker (interactive) or Create new parameter helper object, a new coordinate parameter / marker is created (see figure Coordinate parameters). These coordinate parameters can be used as object or task parameters. For example, the button can be found in the objects tab as well as in the tasks tab (as task parameters).
Add marker (interactive) or Create new parameter helper object, a new coordinate parameter / marker is created (see figure Coordinate parameters). These coordinate parameters can be used as object or task parameters. For example, the button can be found in the objects tab as well as in the tasks tab (as task parameters).
An existing coordinate parameter is selected from the 3D scene via the button ![]() Select parameter.
Select parameter.
Coordinate parameters are created as follows:
(1) |
Move the mouse to the intended position and a left click to fix the position. |
(2) |
Move the mouse in the direction of the intended orientation and a left click to select that orientation. |
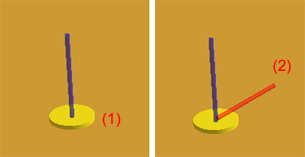
Figure 183: Coordinate parameters
In order to create auxiliary objects / coordinate parameters such as grab points, TCPs or walk points on selected objects, helper objects must first be added via user-defined parameters. This is described in the section Parameter types / User-defined parameters / User-defined object parameters .
Beside their definition in the object parameter section object handling helper objects can be grouped into several types (e. g. grab point, tool center point, walk positions, ...) (see figure Helper objects). Type selection can be made by clicking the circle shaped icon.
Figure 184: Helper objects
The figure below shows the process of grasp point creation (see figure Grab point) and the resulting simulation (see figure Simulation result).
Multiple grasp points can be defined for one or both hands. If grasp points are more than the number of hands required to execute the task, the suitable grasp points are algorithmically selected. If the automatic selection of grasp point is not required, then activate Fix hands.
iAs soon as a grasp point is required but none is defined. six grasp points are created internally in the middle of all six surfaces of the bounding box. An algorithm decides which of the internal grasp points will be used. When picking up markers, they are treated as an object and two grasp points (one each for left an right hand) are created internally with the same orientation as the marker. |
When searching for the best grasp point, grasp points that are explicitly defined for the active hand are prioritized. Only if there are no such gripping points are the remaining ones taken into account in the search.
Prioritization of grasp points according to creation type:
1. The highest priority is given to grasp points that are added as helper objects (see chapter Parameter types / User-defined parameters / User-defined object parameters).
2. The children of an object have second priority.
3. Third priority is given to grasp points that are explicitly stated in a task.
iEither all of the used grasp points should be created as helper objects or none of them. |
Walk positions (WP) which are defined as helper objects below an object can be used as the target location for the human model. In case of multiple walk targets, the shortest calculated path will be used. In case of no defined walk positions, a target location for the object will be automatically calculated.
Next to the last button used ![]() ,a helper object(s) symbol:
,a helper object(s) symbol: ![]() is displayed after having selected the coordinate parameters. The parameter can be deleted by clicking on the cross in the button.
is displayed after having selected the coordinate parameters. The parameter can be deleted by clicking on the cross in the button.