By starting ema, its user interface is displayed.
iSome of the described functionalities are only visible / active if the corresponding license is available. |
The user interface is basically divided into 5 parts:
1 |
the menu bar |
2 |
the tabs |
3 |
the 3D settings |
4 |
the 3D view |
5 |
task overview |
6 |
the information area (process area and status area) |
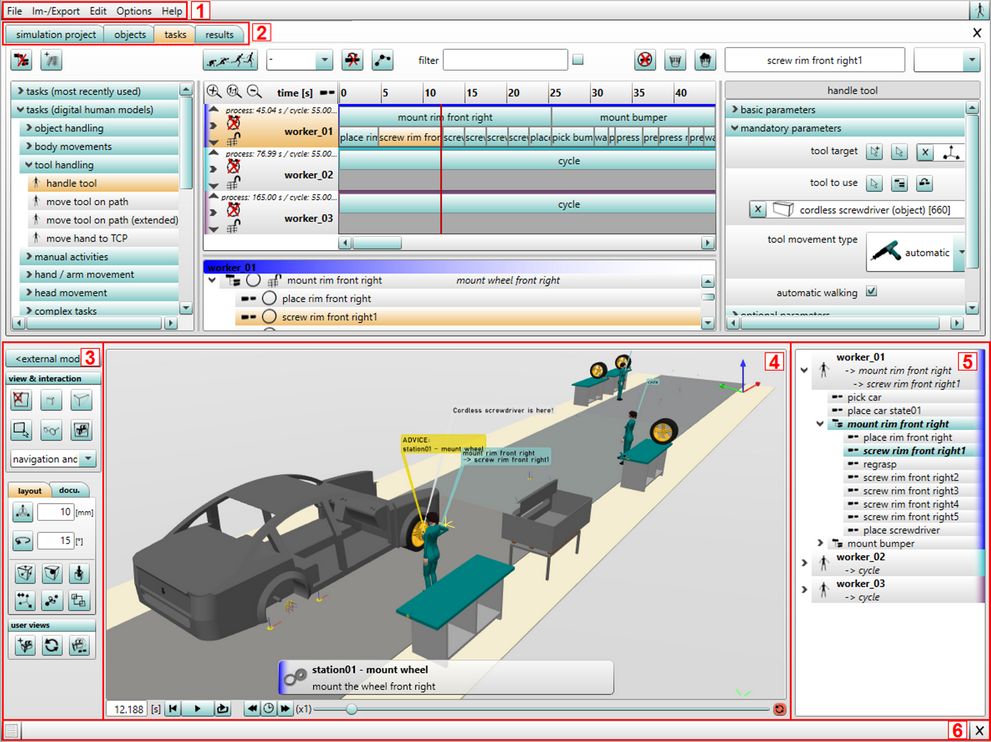
Figure 14: User interface
The following is a brief overview of the chapter User interface and its sub-chapters.
1 The menu bar contains the following menus: File, Edit, Options and Help. A more detailed description is given in the chapter User interface / Menu bar.
2 If one of the tabs Simulation project, Objects, Tasks, Ergonomics or Results is selected, the content of the work area is adapted to the respective task. In the tab Simulation project, master data is generated and stored (see chapter User interface / tab "Simulation Project"). The tab Objects allows the adding and replacement of the simulation objects (see chapter User interface / tab "Objects"). These simulation objects can be either displayed as list or as tree structure. The user-based composition of the tasks to be simulated is realised in the tab Tasks (see chapter User interface / tab "Tasks"). For that purpose, task bars are available for each human model, which can be filled with tasks from a performance library by drag and drop. By clicking on the button Simulate, the process of posture generation starts for all human models. A summary of the simulation procedure and the calculated parameters (time, added value, etc.) can be considered in the tab Results (see chapter User interface / tab "Results"). Evaluations of the simulation with respect to posture or ergonomics values as well as the forces and loads can be realised in the sub tab Ergonomics.
3 The area 3D settings allows the control of the simulation playback (see chapter User interface / 3D settings).
4 In the area 3D view, the 3D simulation is played back (see User interface / 3D view). For this process, distinction must be made between an internal and an external mode.
5 In the Task overview the currently used tasks are listed. The tasks can be selected and will be synchronized with the end posture of the selected task in the 3D main window.
6 The Information area is divided into the process area and the status area. The process area outputs information on the progress of the ema activities similarly to a log file and when applicable, it signals the occurrence of errors (see chapter User interface / Process area). In the status area, duration and progress of processing procedures are visualised by means of status bars during the execution of the program (see chapter User interface / Status area).